Temporal Convolutional Network Based Signal Detection for Magnetotactic Bacteria Communication System
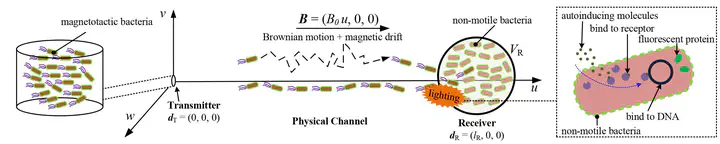 The whole framework.
The whole framework.Abstract
Molecular communication (MC) aims to use signaling molecules as information carriers to achieve communication between biological entities. However, MC systems severely suffers from inter symbol interference (ISI) and external noise, making it virtually difficult to obtain accurate mathematical models. Specifically, the mathematically intractable channel state information (CSI) of MC motivates the deep learning (DL) based signal detection methods. In this paper, a modified temporal convolutional network (TCN) is proposed for signal detection for a special MC communication system which uses magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) as information carriers. Results show that the TCN-based detector demonstrates the best overall performance. In particular, it achieves better bit error rate (BER) performance than sub-optimal maximum a posteriori (MAP) and deep neural network (DNN) based detectors. However, it behaves similar with the bidirectional long short term memory (BiLSTM) based detector that have been previously proposed and worse than the optimal MAP detector. When both BER performance and computational complexity are taken into account, the proposed TCN-based detector outperforms BiLSTM-based detectors. Furthermore, in terms of robustness evaluation, the proposed TCN-based detector outperforms all other DL-based detectors.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.